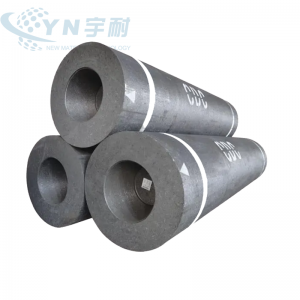
HP Graphite Electrode
The production process of graphite electrodes generally includes: raw material (wool) → batching → kneading → extrusion molding → high temperature sintering (1550~1700°C) + heat treatment (1100~1200°C) + finishing.
1. Wool pretreatment: remove the impurities in the wool. The main method of impurities is to use water washing or alkali washing.
2. Ingredients: Add a certain amount of quartz sand when kneading, and put the mixed raw materials into the kneading equipment for kneading.
3. Kneading: Put the mixed raw materials into the center of the graphite extruder, and then knead and extrude the kneaded raw materials to form them in the graphite mold.
4. Roasting: Burn the mixed material with charcoal into red heat or combustible substances such as carbon black and charcoal powder, and then enter the next process.
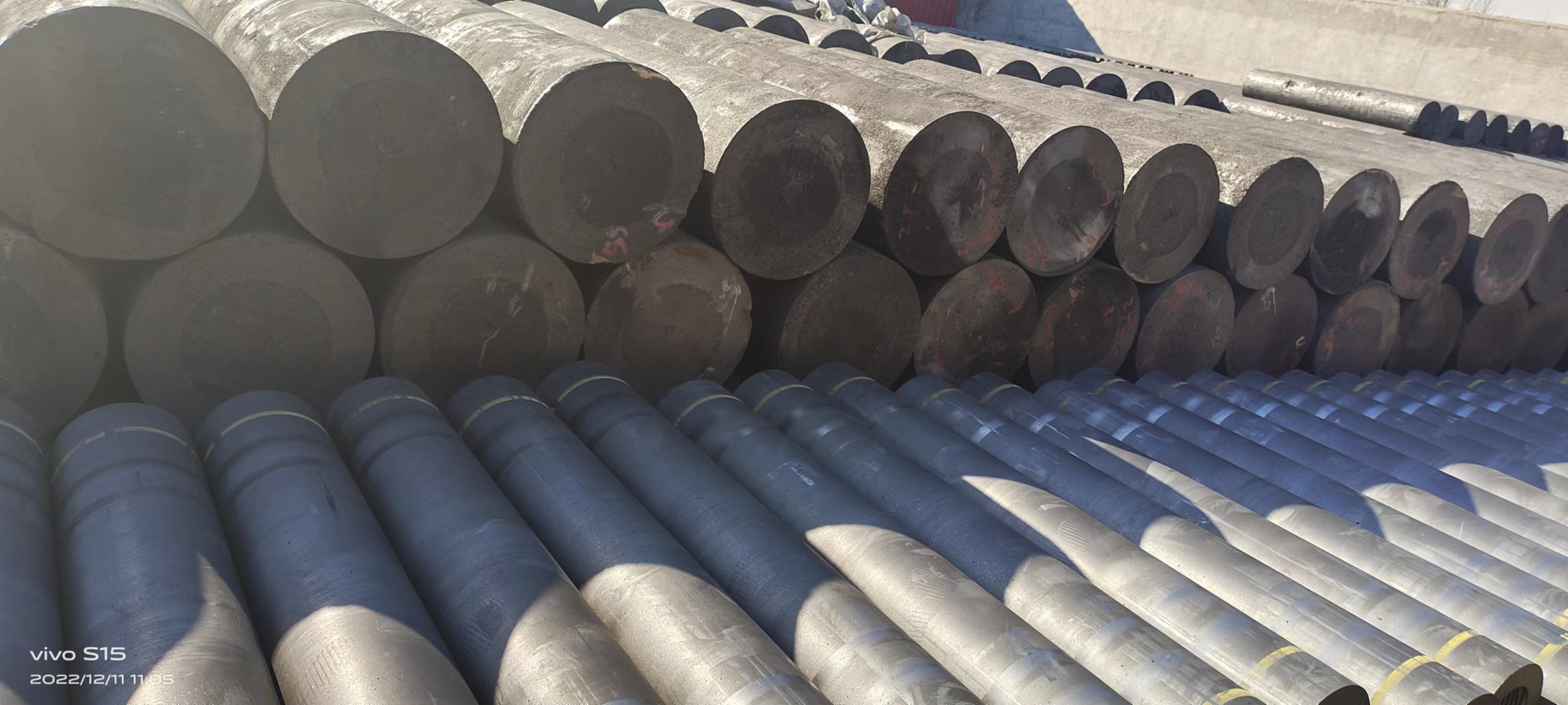
5. Finishing: After the mold is formed, it needs to be cut, welded, polished and other processes.
6. Packaging: Molds must be inspected (including cleanliness and whether there are any damages and scratches, etc.) and sorted and stacked before they can be stored in the warehouse.
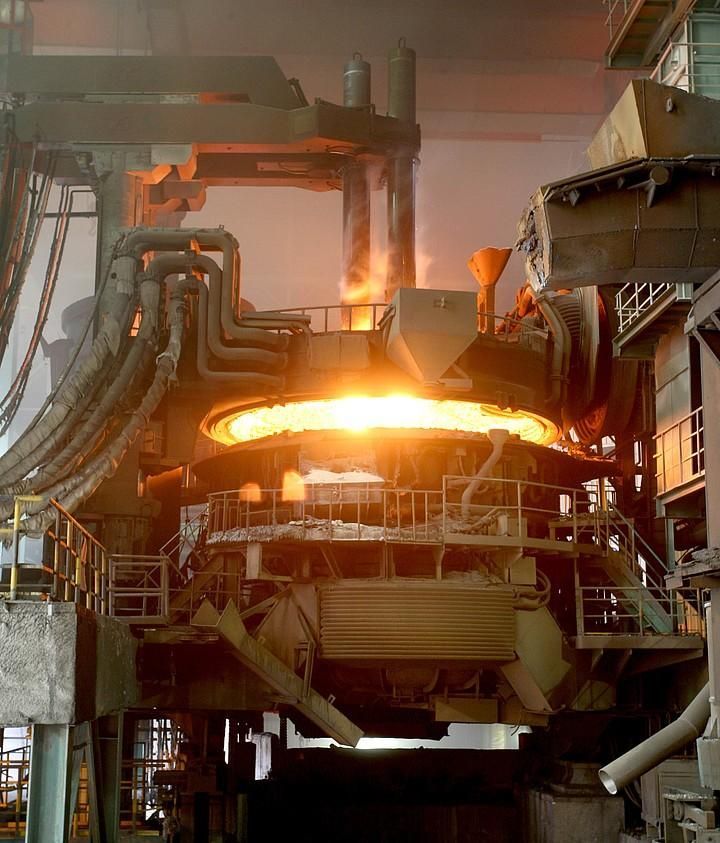


The functions of the carbonization charge layer are: to protect the charge from oxidation at high temperature, so as to ensure that the metal elements in the slag will not volatilize; to maintain the carbothermal reduction reaction in the molten state, to ensure that the charge is smelted at the optimum temperature and time.
The main function of the electric arc furnace is to introduce an electric arc into the charge to melt the molten carbon steel material into a metal alloy. The electrode material of electric arc furnace is generally graphite electrode, anode and cathode graphite.
Carbonization furnace: charcoal is burned in the furnace to generate carbon and oxygen, and the generated flue gas enters the molten pool after cooling, and the molten steel is discharged outward at the same time.
Rotary Kiln: A reduction kiln is used in the smelting process for smelting metals or alloys.






 Quote Now
Quote Now